Pulmonary function tests PFT:
Pulmonary function tests are a group of
tests that measure how well the lungs take in and release air and how well they
move gases such as oxygen from the atmosphere into the body's circulation.
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS The
major types of pulmonary function tests include spirometry, measurement of lung
volumes, and quantitation of diffusing capacity. Measurements of maximal
respiratory pressures and flow-volume loops, which record forced inspiratory
and expiratory flow rates, are also useful in specific clinical circumstances.
Spirometry
Spirometry includes tests of pulmonary
mechanics – measurements of FVC, FEV1, FEF values, forced inspiratory flow
rates (FIFs), and MVV. Measuring pulmonary mechanics assesses the ability of
the lungs to move large volumes of air quickly through the airways to identify
airway obstruction.
The measurements taken by the spirometry
device are used to generate a pneumotachograph that can help to assess lung
conditions such as: asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Physicians may also use the test results to
diagnose bronchial hyperresponsiveness to exercise, cold air, or pharmaceutical
agents
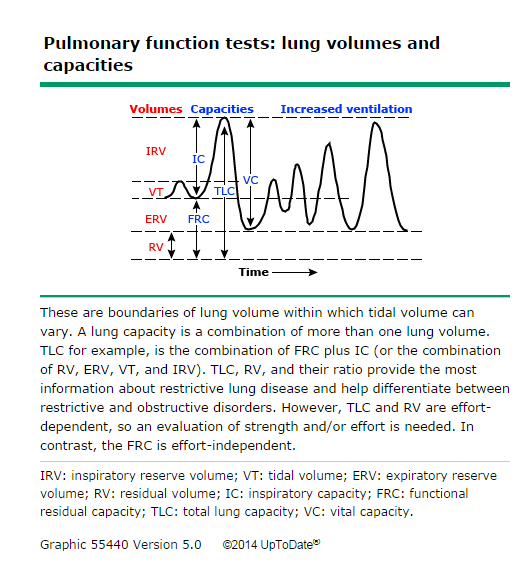
Lung volumes
Common lung volume measurements include
total lung capacity (TLC), functional residual capacity (FRC), and residual
volume (RV) . Measurement of the total lung capacity (TLC) may be helpful when
the vital capacity is decreased. For example, in the setting of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with a low vital capacity, measurement of
the TLC can help determine if there is a superimposed restrictive disorder.
There are four methods of measuring TLC:
●Helium dilution
●Nitrogen washout
●Body plethysmography
●Chest radiograph measurements
The first two methods are used extensively
in hospital pulmonary function laboratories, but they may underestimate the TLC
in patients with moderate to severe COPD. The gold standard for measurement of
TLC, particularly in the setting of significant airflow obstruction, is body
plethysmography.
Measurements of TLC using the chest
radiograph or high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) correlate within 15
percent of those obtained by body plethysmography . Since the TLC is equivalent
to the amount of air seen in the lungs on a chest radiograph taken at maximal
inspiration, it is important that the subject inhales maximally as the image is
created.
Pulmonary function tests is an inclusive
term that refers to several different procedures that measure lung function in
different ways. Some of the more common values that may be measured during
pulmonary function testing include:
·
Tidal volume (VT). This is the amount of air inhaled
or exhaled during normal breathing.
·
Minute volume (MV). This is the total amount of air
exhaled per minute.
·
Vital capacity (VC). This is the total volume of air
that can be exhaled after maximum inspiration.
·
Functional residual capacity (FRC). This is the amount
of air remaining in lungs after normal expiration.
·
Total lung capacity. This is the total volume of lungs
when maximally inflated.
·
Forced vital capacity (FVC). This is the amount of air
exhaled forcefully and quickly after maximum inspiration.
·
Forced expiratory volume (FEV). This is the volume of
air expired during the first, second, and third seconds of the FVC test.
·
Forced expiratory flow (FEF). This is the average rate
of flow during the middle half of the FVC test.
·
Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR). This is the maximum
volume during forced expiration.
The normal values for PFTs vary from person
to person. The amount of air inhaled and exhaled in your test results are
compared to the expected average in someone of the same age, height, sex, and
race. In addition, results are compared to your previous test results, if
previous testing has been done. If you have abnormal PFT measurements or if
your results are different from previous tests, you may be referred for other
diagnostic tests to establish a medical diagnosis.
Reasons for the procedure
There are many different reasons why PFTs
may be ordered. They are sometimes ordered in healthy individuals as part of a
routine physical. In others, the tests may be ordered when a specific illness
is suspected. Some of the disorders that may be detected with PFTs include, but
are not limited to, the following:
·
Allergies. An acquired, abnormal immune response to
one or more substances that can cause a broad range of inflammatory reactions.
·
Chronic lung conditions. Conditions, such as asthma,
bronchiectasis, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis, that can be treated but not
cured.
·
Asbestosis. A lung disease caused by the inhalation of
asbestos fibers.
·
Chest trauma. Trauma to the chest, such as fractured
ribs or a recent surgical procedure, can restrict an individual’s ability to
breathe adequately.
·
Restrictive airway conditions. Impaired lung expansion
as a result of conditions, such as scoliosis, pulmonary tumors, or inflammation
or scarring of the chest wall.
·
Respiratory infections.
·
Sarcoidosis. A condition that causes small, fleshy
swellings in the tissue around the organs, usually in the liver, lungs, and
spleen.
·
Scleroderma. A disease of the body’s connective tissue
that causes thickening and hardening of the skin.
·
PFTs may be used to assess the lung function of
patients prior to surgery or other invasive procedures in patients who have
current lung and/or heart problems, who are smokers, or who have other
conditions that might be affected by surgery or other procedures.
·
Another use of PFTs is the evaluation of treatment for
conditions such as asthma, emphysema, and other chronic lung problems.
·
There may be other reasons for your doctor to
recommend pulmonary function tests.
Before the procedure
·
Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and
offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the
procedure.
·
Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting,
fluid restriction, or sedation is required. However, you may be asked to avoid
eating a heavy meal before the test.
·
If you are pregnant or suspect that you may be
pregnant, you should notify your doctor.
·
Notify your doctor of all medications (prescription
and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking.
·
If you are a smoker, you will usually be asked to
refrain from smoking for a period of time before the test.
·
Your height and weight will be recorded so that your
results can be accurately calculated.
·
Based on your medical condition, your doctor may
request other specific preparation.
During the procedure
Pulmonary function tests may be done on an outpatient
basis or as part of your stay in the hospital. Procedures may vary depending on
your condition and your and your doctor’s practices.
Generally, PFTs follow this process:
·
You will be asked to loosen tight clothing, jewelry,
or other objects that may interfere with the procedure
·
If you wear dentures, you will be asked to wear them
during the procedure.
·
You will be asked to empty your bladder before the
procedure to optimize comfort.
·
You will sit in a chair or stand for the procedure.
·
You will be given a soft nose clip to wear during the
procedure so that all of your breaths will go through your mouth, rather than
your nose.
·
You will be given a sterile mouthpiece that will be
attached to the spirometer.
·
With your mouth forming a tight seal around the
mouthpiece, you will be instructed to perform various breathing maneuvers. The
maneuvers will be done by inhaling and exhaling. Depending on what measurements
are ordered, you may be asked to repeat the maneuvers several times before the
test is completed.
·
You may be given a bronchodilator after certain tests
have been performed. These tests will be repeated several minutes later after
the bronchodilator has taken effect.
·
You will be monitored carefully during the procedure
for faintness, dizziness, difficulty breathing, or any other problems.
After the procedure
Generally, there is no special type of care following PFTs. You may
resume your usual diet, medications, and activities unless your doctor advises
you otherwise.
If you have a history of respiratory problems, you may be tired after
the procedure. You will be given the opportunity to rest afterwards.
Your doctor may give you additional or alternate instructions after the
procedure depending upon your particular situation.
Ref :
UPTODATE
hopkinsmedicine


























0 comments:
Post a Comment